You’re saddling up for a journey into the future, where horse-drawn buggies are replaced by vehicles equipped with cutting-edge backup cameras. As you dive into this guide, you’ll learn how to pick the perfect camera to safeguard your rides.
You’ll need to weigh the pros and cons of different models, ponder installation ease, and think about the clarity of the video feed, especially in the dead of night. We’ll help you understand the importance of a wide viewing angle and the choice between wired or wireless setups.
Let’s navigate the landscape of backup cameras together, ensuring you’re well-equipped to make a savvy purchase. This guide is your roadmap to a backup camera that fits seamlessly with your vehicle and your driving habits.
Key Takeaways
- Backup cameras come in two main types: CCD and CMOS sensors, with CCD sensors offering better image quality and CMOS sensors being more cost-effective.
- When evaluating backup cameras, consider the variety of camera types available, such as license plate cameras and bumper-mounted options, and scrutinize the horizontal viewing angle for maximum coverage.
- Sensor technology plays a crucial role in image quality and performance in low-light conditions, with CCD sensors providing excellent image quality and CMOS sensors being less costly and consuming less power.
- The viewing angle of a backup camera determines the area that can be seen while reversing, so aim for a camera with at least a 120-degree viewing angle for comprehensive coverage and consider models with adjustable brackets for flexibility.
Understanding Backup Cameras
To ensure you’re making an informed purchase, it’s crucial to grasp how backup cameras work and the features they offer. These devices, also known as a rear-view camera, activate when you shift your vehicle into reverse, providing a video feed of what’s behind you.
The types of backup cameras range from simple camera-only setups to comprehensive systems with screens and sensors. Two main types of image sensors are used: CCD or CMOS. CCD sensors are known for better quality images, while CMOS sensors are usually more cost-effective.
The sensors convert light into signals, giving you a clear picture even in low-light conditions. Many backup cameras also come with a selectable parking lines feature, enhancing your ability to gauge distance and maneuver into tight spaces.
It’s important to consider the field of view as well, which depends on the sensor size and lens focal length. A larger sensor generally means a wider field of view and improved performance when lighting is poor.
When shopping for a backup camera, look for one that matches your needs for safety, convenience, and budget.
Evaluating Camera Types
You’ll find a variety of camera systems to choose from, each offering different features and benefits.
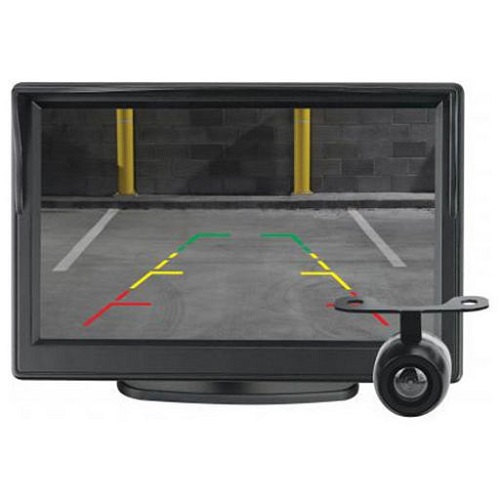

It’s crucial to understand the sensor technology differences, as they’ll affect image quality and performance in low-light conditions. Plus, the viewing angle options will determine how much of the area behind your vehicle you can actually see.
Camera System Variety
When evaluating backup camera types, it’s essential to consider the variety available to find the perfect fit for your vehicle and driving needs. Camera system variety is vast, with types of backup cameras ranging from license plate cameras to bumper-mounted options. You’ll want to scrutinize the horizontal viewing angle to ensure maximum coverage behind your vehicle.
Additionally, the choice between CCD or CMOS sensors can impact image quality, especially in low-light conditions. License plate cameras are discreet and easy to install, but make sure they don’t obscure your plate.
Sensor Technology Differences
Understanding the difference between CCD and CMOS sensors is crucial as you evaluate backup camera options for your vehicle. CCD, or Charge-Coupled Device sensors, are known for their excellent image quality. They convert light to signal with high precision, offering clarity especially in low-light conditions. However, they can be more expensive and sensitive to image noise, which could be a drawback in certain environments.
On the other hand, CMOS, or Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor sensors, are generally less costly and consume less power. While they’ve historically been less sharp than their CCD counterparts, advancements have significantly improved their quality.
When comparing sensor technology differences, weigh the importance of image quality against cost and power consumption to find the best match for your needs.
Viewing Angle Options
Evaluating the viewing angle of your backup camera is paramount as it determines the expanse of the area you’ll be able to monitor while reversing. You’ll find a wide variety of backup cameras, each boasting different viewing angles. For comprehensive coverage, you should aim for a camera with at least a 120-degree viewing angle.
Some models come with an adjustable bracket, offering flexibility to achieve the perfect angle for your specific vehicle. Consider cameras that fit over your license plate using a seamless design, which often provide a broad viewing angle without the need for extensive modifications.

Always check the camera feed quality to ensure that the wider viewing angle doesn’t compromise the image clarity. The right balance will give you a sweeping view, enhancing safety and convenience.
Key Feature Considerations
As you weigh your options for a backup camera, image quality should be at the forefront of your considerations. You’ll want to ensure that the camera’s night vision capabilities are robust enough to provide clear visibility in low-light conditions.
Image Quality Importance
Image quality is crucial in backup cameras, as it determines how clearly you’ll see potential hazards behind your vehicle. When you’re shopping for a backup camera, understanding the image quality importance can’t be overstated.
A camera’s sensor technology, be it CCD or CMOS, plays a pivotal role. CMOS sensors are known for their superior performance in low light, which is essential for those twilight hours or shadowed areas.
Additionally, pay close attention to the lux rating; a lower lux means the camera will give you a clearer picture in dimly lit conditions. Don’t overlook this, especially since you’ll often rely on your backup camera in varying lighting.
Night Vision Capability
When you’re backing up in low-light conditions, a backup camera with strong night vision capabilities is crucial for your safety. As you evaluate different backup camera systems, consider the importance of a camera that provides a clear view even at night. A camera equipped with infrared or LED lights can significantly enhance your night vision. Look for features like HDR or WDR, which can improve the camera’s performance in varying light levels during parking.
Make sure to check whether the backup camera uses a CCD or CMOS sensor; CCD is often superior for low-light conditions. Additionally, a camera with mirror image capability can make nighttime reversing more intuitive, closely resembling what you’d see in a rearview mirror. These features combined will ensure your backup camera system is effective, no matter the time of day.

Assessing Installation Requirements
Before you commit to a backup camera, you’ll need to gauge your DIY skill level to determine if you can handle the installation yourself or if you should budget for professional help. Installing a backup camera often involves running cables and mounting hardware, which can be a straightforward task for some but daunting for others. Consider the cost of professional installation as well, as it can vary widely based on the complexity of the system and your vehicle type.
DIY Skill Level
You’ll need a solid grasp of automotive electronics to tackle the installation of a backup camera on your own. Installing a backup system requires precision and an understanding of your vehicle’s wiring. For wired systems, you’ll run cables from the monitor to the vehicle’s power source and connect to the backup light circuit. This ensures the camera activates when you shift into reverse.
If you opt for a wireless backup camera, installation is simpler, but you’ll still need to connect the camera to a power source. Be ready to handle video inputs and configure the display. With the right tools and a careful approach, you can install a backup camera successfully, enhancing your safety on the road.
Professional Installation Cost
Typically, you’ll find that professional installation costs for backup cameras can vary widely, depending on your vehicle’s make and model as well as the complexity of the system you’ve chosen.
When you’re backup camera buying, remember that installing a new system could mean labor charges around $75 per hour. The intricacy of rear-view cameras and the type of display they’re connected to can impact the installation time, thus affecting the overall professional installation cost.
If your camera is simple and your vehicle readily accommodates aftermarket additions, you might be looking at a lower cost. However, when putting your vehicle into reverse, you want a seamless experience. Ensure compatibility to avoid extra expenses that come with complex integration.
Video Quality and Sensors
As you navigate the market for backup cameras, video quality and sensor technology are key features you’ll want to scrutinize. High resolution and clarity in the camera’s display ensure you get a crisp, clear view of what’s behind you, especially in challenging lighting conditions. Let’s compare sensor types and explore night vision capabilities to find the perfect match for your safety needs.
Resolution and Clarity
When selecting a backup camera, it’s crucial to consider both the resolution and the type of sensor, as these determine the clarity of the image you’ll see. CCD sensors typically offer higher video quality, especially in low light conditions, compared to CMOS sensors. This distinction is vital as you’ll rely on your camera to navigate through darker environments.
The sensor size impacts resolution and clarity; a larger sensor captures more information, providing a clearer picture of what’s behind your vehicle. Moreover, the question of which sensor is better for your needs hinges on the balance between resolution and environmental factors. A camera with a high resolution and a sensitive sensor will ensure that you have a crisp, clear view whenever you’re reversing.
Night Vision Capability
Building on the importance of resolution and sensor type for clarity, you’ll also want to ensure your backup camera is equipped with night vision capabilities to maintain that sharpness after dusk.
When shopping for a new backup camera, examine whether the cameras use either CCD or CMOS sensors, as this will affect your night-time visibility. A CCD sensor generally outperforms a CMOS in low light, rendering a clearer image on your view mirror.
Look for cameras with a low LUX rating, indicating superior low-light performance. Additionally, consider models with built-in LED or infrared lights, which boost night vision capability. This technology allows you to reverse safely, with a clear view, no matter how dark it’s outside.
Sensor Type Comparison
Understanding the differences between CCD and CMOS sensors is crucial as you’ll encounter both types when choosing a backup camera. CCD sensors are renowned for their high-quality video, especially in low-light conditions. They’re the go-to for a clearer image, making them a top pick in sensor type comparison for backup cameras.

On the other hand, CMOS sensors are more cost-effective, but you’ll notice a drop in video quality and performance. When delving into camera systems, remember that CCD options tend to offer superior visuals. If you prioritize video quality and reliability in various lighting, CCD is the way to go. However, for those on a budget, CMOS still provides a functional solution, albeit with compromises. Choose wisely to ensure your backup camera system meets your expectations.
Choosing a Mounting Position
Now, let’s focus on where to mount your backup camera for the best results. You’ve got options like integrating it with your license plate or choosing between a bumper and tailgate mount. Each position offers distinct advantages and challenges, so consider your vehicle’s design and your visibility needs carefully.
License Plate Integration
While deciding where to mount your backup camera, consider the license plate integration for its straightforward installation process. This method typically involves a strap mount that attaches directly to your existing license plate using its screws, fitting snugly in the inset area.
It’s an ideal choice if you’re looking for a mounting position that doesn’t require drilling or complex modifications to your vehicle. Ensure you choose the right backup camera that aligns with the dimensions and aesthetics of your matching license plate for a cohesive look.
License plate integration not only simplifies the installation but also maintains the original appearance of your car, making it an attractive option for many drivers.
Bumper Vs. Tailgate Mount
After considering license plate integration for its ease of installation, you’ll want to decide between a bumper or tailgate mount to best suit your visibility needs and vehicle design.
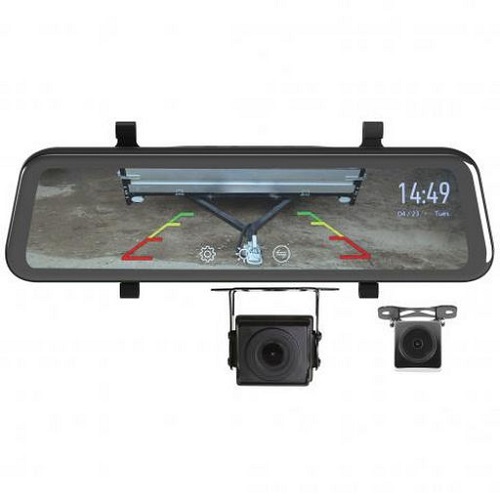

Bumper mounted backup cameras are favored for their ability to eliminate the rear blind zone, broadening your rear view significantly. They integrate well with various vehicle types and provide a reliable, wide-angle perspective that’s essential for safe reversing.
Alternatively, tailgate-mounted cameras offer the convenience of use at any time, not just when you’re backing up. This type of mount is particularly flexible, adapting to different situations, such as monitoring a towed trailer.
Wired Vs Wireless Options
Now you’re faced with a choice between wired and wireless backup cameras, each with its own set of considerations. You’ll need to weigh the ease of installation offered by wireless systems against the consistent signal quality of a wired setup. Also, think about how different power sources will affect the camera’s operation and your overall convenience.
Installation Complexity
Although you might be eager to enhance your vehicle’s safety with a backup camera, you’ll need to decide whether a wired or wireless system better suits your installation skills and patience.
Wired backup cameras involve more installation complexity, requiring you to run a wire from the camera to your vehicle’s power source and backup light circuit. You’ll need a grasp of basic automotive repair and electronics to manage the task.
On the other hand, wireless options reduce the hassle, especially in larger vehicles like trucks or RVs. Regardless of your choice, you’ll typically be provided with an adjustable bracket and instructions for connecting to your vehicle’s video input.
Signal Reliability
Your vehicle’s safety upgrade requires a dependable signal, and choosing between a wired and wireless backup camera system is crucial for consistent performance.
Wired backup cameras typically offer more reliable signal transmission, minimizing disruptions and ensuring the video feed isn’t affected by interference. This could be critical when you’re relying on your camera’s CCD or CMOS sensors to deliver clear images, even in challenging weather or low-light conditions.
Wireless options might tempt you with their ease of installation, but they can be susceptible to signal dropouts, which could spell trouble when you’re counting on those active parking lines to guide you.
Power Source Differences
When choosing between wired and wireless backup cameras, you’ll need to consider the differences in their power sources.
Wired systems draw directly from your vehicle’s electrical system and often use CCD or CMOS sensors. They generally require less power than other devices in your car. However, you’ll still have to wire the system to the vehicle’s power source, which can be a complex task if you’re not familiar with automotive electronics.
On the other hand, wireless cameras typically rely on batteries or separate power connections. While they offer more flexibility in terms of installation, they might necessitate frequent battery changes or ensuring a constant external power source. This can add to maintenance efforts.
Always weigh these power source differences before making your decision.
Finding the Right Retailer
Selecting the right retailer is crucial for purchasing a backup camera that meets all your vehicle’s needs. When you’re in the market for a new rear camera, it’s essential to choose the right store to ensure you get a high-quality product along with reliable service.
Campad Electronics stands out as a retailer that offers an extensive selection of backup cameras, catering to various vehicle makes and models. They provide you with options ranging from camera-only systems to all-in-one solutions, ensuring you’ll find the different types of backup cameras suited to your specific requirements.
Shopping online with Campad Electronics simplifies the process, allowing you to compare various models conveniently. Plus, their expertise means that you’ll have access to professional support for installation issues. This is particularly beneficial if you encounter any technical challenges when fitting your new rear camera.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Choose a Backup Camera?
You’ll want to consider the camera’s view angle, image quality, and whether it has night vision. Make sure it’s compatible with your vehicle and think about ease of installation before you buy.
What Is Best Brand of Backup Camera?
You’ll find that brands like Garmin, Yada, AUTO-VOX, Garmin, Furrion, BOSCAM, Strike, EWAY, LeeKooLuu and eRapta are highly regarded for backup cameras, offering quality, reliability, and a range of features to suit different needs and budgets.
What to Look for When Buying a Reverse Camera?
When you’re buying a reverse camera, prioritize video quality, low-light performance, sensor type, and a wide field of view. Ensure it’s compatible with your vehicle and consider ease of installation and cost.
What Is the Difference Between a Backup Camera and a Rear View Camera?
You’re wondering about the difference? A backup camera activates in reverse, giving a clear, wide view to help with parking. A rear-view camera can be used anytime, offering more flexible viewing options.
Conclusion
You’re all set to enhance your safety with the perfect backup camera. Remember to weigh the camera types, key features, and installation needs that best match your ride. Prioritize video quality and choose a mounting spot that offers the best view.
Decide between the reliability of wired or the convenience of wireless. Lastly, pick a reputable retailer for your purchase. Drive with confidence, knowing you’ve made a smart choice for a safer reverse.

Hey there, I’m Terra Frank, the driving force behind Motion Performance Motor Sports. I’m thrilled to have you here, exploring the fascinating world of cars, trucks, and everything related to automotive performance and accessories.




